Description
C2 Ceramide (Ceramide 2) is the main lipid of the stratum corneum and a protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) activator. C2 Ceramide activates PP2A and ceramide-activated protein phosphatase (CAPP). C2 Ceramide induces cells differentiation and apoptosis, inhibits mitochondrial respiratory chain complex III. C2 Ceramide is also a skin conditioning agent that protects the epidermal barrier from water loss.
Product information
CAS Number: 3102-57-6
Molecular Weight: 341.53
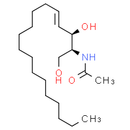
Formula: C20H39NO3
Synonym:
Ceramide 2
Chemical Name: N-[(2S, 3R, 4E)-1, 3-dihydroxyoctadec-4-en-2-yl]acetamide
Smiles: CCCCCCCCCCCCC/C=C/[C@@H](O)[C@H](CO)NC(C)=O
InChiKey: BLTCBVOJNNKFKC-QUDYQQOWSA-N
InChi: InChI=1S/C20H39NO3/c1-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-20(24)19(17-22)21-18(2)23/h15-16,19-20,22,24H,3-14,17H2,1-2H3,(H,21,23)/b16-15+/t19-,20+/m0/s1
Technical Data
Appearance: Solid Power
Purity: ≥98% (or refer to the Certificate of Analysis)
Solubility: DMSO : 20 mg/mL (58.56 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) Ethanol : 17 mg/mL (49.78 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming)
Shipping Condition: Shipped under ambient temperature as non-hazardous chemical or refer to Certificate of Analysis
Storage Condition: Dry, dark and -20 oC for 1 year or refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Shelf Life: ≥360 days if stored properly.
Stock Solution Storage: 0 - 4 oC for 1 month or refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Drug Formulation: To be determined
HS Tariff Code: 382200
How to use
In Vitro:
C2 Ceramide (5 nM-200 µM; 24 hours; primary mouse osteoblasts) treatment (≤500 nM) promots osteoblast viability, whilst concentrations ≥2 µM significantly reduces osteoblast viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner. C2 Ceramide increases cytoplasmic histone-associated DNA fragments by 5.7- and 11.2-fold at 50 µM and 100 µM C2 Ceramide concentrations respectively in osteoblasts. At these higher concentrations, C2 Ceramide is a potent inducer of apoptosis in osteoblasts[1]. C2 Ceramide up-regulates mRNA expression of angiogenic genes in human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) and increases the migration and capillary tube formation of endothelial cells, whereas PP1 small interfering RNA shows opposite effects. Human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) increases levels of bone morphogenetic protein 2, phosphorylation of Smad 1/5/8, and mRNA expression of runt-related transcription factor 2 and osterix.
In Vivo:
The PP1 activator C2 Ceramide increases alkaline phosphatase activity, mineralizes nodule formation, and mRNA expression of dentin matrix protein 1 and dentin sialophosphoprotein. In contrast, knockdown by PP1 small interfering RNA inhibits odontoblastic differentiation.
References:
- P A Hill, et al. Ceramide-induced Cell Death/Survival in Murine Osteoblasts. J Endocrinol. 2010 Aug;206(2):225-33.
- Ji-Youn Kim, et al. Role of Protein Phosphatase 1 in Angiogenesis and Odontoblastic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Cells. J Endod. 2017 Mar;43(3):417-424.
- R T Dobrowsky, et al. Ceramide Stimulates a Cytosolic Protein Phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5048-51.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use.
Payment & Security
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.