Description
Aloxistatin (E-64d), is a selective cysteine protease inhibitor or calpain and autophagy inhibitor. E-64d prevents in vitro cerulein- induced trypsinogen activation. E-64d can enter the intact cell and inhibit calpain. E-64d has been shown safe for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease in human. E-64d is potentially useful in the treatment of developmental seizure-induced brain damage both by regulating abnormal zinc signal transduction and through the modulation of altered lipid metabolism via ApoE/clusterin pathway in hippocampus.
Product information
CAS Number: 88321-09-9
Molecular Weight: 342.43
Formula: C17H30N2O5
Synonym:
E-64d
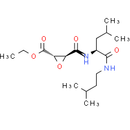
Chemical Name: ethyl (2S, 3S)-3-(((S)-1-(isopentylamino)-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl)carbamoyl)oxirane-2-carboxylate
Smiles: CCOC(=O)[C@H]1O[C@@H]1C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)NCCC(C)C
InChiKey: SRVFFFJZQVENJC-IHRRRGAJSA-N
InChi: InChI=1S/C17H30N2O5/c1-6-23-17(22)14-13(24-14)16(21)19-12(9-11(4)5)15(20)18-8-7-10(2)3/h10-14H,6-9H2,1-5H3,(H,18,20)(H,19,21)/t12-,13-,14-/m0/s1
Technical Data
Appearance: Solid Power
Purity: ≥98% (or refer to the Certificate of Analysis)
Solubility: DMSO: 68 mg/mL(198.58 mM).
Shipping Condition: Shipped under ambient temperature as non-hazardous chemical or refer to Certificate of Analysis
Storage Condition: Dry, dark and -20 oC for 1 year or refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Shelf Life: ≥12 months if stored properly.
Stock Solution Storage: 0 - 4 oC for 1 month or refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Drug Formulation: To be determined
HS Tariff Code: 382200
How to use
In Vitro:
Aloxistatin can enter the intact platelet and inhibit proteolysis by inhibiting calpain. Aloxistatin blunts Parathyroid hormone (PTH)-induced cell proliferation and inhibits differentiation osteoblasts in vitro.
In Vivo:
Aloxistatin (100 mg/kg, p.o.) strongly inhibits the cathepsin B&L activities in the skeletal muscle, heart and liver of hamsters. In spinal cord injury (SCI) rats, Aloxistatin provides neuroprotection in SCI lesion and penumbra. Aloxistatin reduces brain amyloid-β and improves memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease animal models by inhibiting cathepsin B activity.
References:
- Murray EJ, et al. Metabolism. 1997 , 46(9), 1090-1094.
- McGowan EB, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989, 158(2), 432-435.
- Tamai M, et al. J Pharmacobiodyn. 1986, 9(8), 672-677.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use.
Payment & Security
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.