Description
Heparin is a sulfated polysaccharide that has been used as a life-saving anticoagulant in clinics well before its detailed structure was known.
Product information
CAS Number: 9005-49-6
Molecular Weight: 1134.93
Formula: C26H42N2O37S5
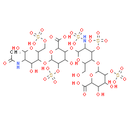
Chemical Name: 3-[(5-{[6-carboxy-4,5-dihydroxy-3-(sulfooxy)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(sulfoamino)-4-(sulfooxy)oxan-2-yl)oxy]-6-({5-acetamido-4,6-dihydroxy-2-[(sulfooxy)methyl]oxan-3-yl}oxy)-4-hydroxy-5-(sulfooxy)oxane-2-carboxylic acid
Smiles: CC(=O)NC1C(O)OC(COS(O)(=O)=O)C(OC2OC(C(OC3OC(CO)C(OC4OC(C(O)C(O)C4OS(O)(=O)=O)C(O)=O)C(OS(O)(=O)=O)C3NS(O)(=O)=O)C(O)C2OS(O)(=O)=O)C(O)=O)C1O
InChiKey: HTTJABKRGRZYRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChi: InChI=1S/C26H42N2O37S5/c1-4(30)27-7-9(31)13(6(56-23(7)39)3-55-67(43,44)45)58-26-19(65-70(52,53)54)12(34)16(20(62-26)22(37)38)60-24-8(28-66(40,41)42)15(63-68(46,47)48)14(5(2-29)57-24)59-25-18(64-69(49,50)51)11(33)10(32)17(61-25)21(35)36/h5-20,23-26,28-29,31-34,39H,2-3H2,1H3,(H,27,30)(H,35,36)(H,37,38)(H,40,41,42)(H,43,44,45)(H,46,47,48)(H,49,50,51)(H,52,53,54)
Technical Data
Appearance: Solid Power
Purity: ≥98% (or refer to the Certificate of Analysis)
Solubility: Soluble in DMSO
Shipping Condition: Shipped under ambient temperature as non-hazardous chemical or refer to Certificate of Analysis
Storage Condition: Dry, dark and -20 oC for 1 year or refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Shelf Life: ≥12 months if stored properly.
Stock Solution Storage: 0 - 4 oC for 1 month or refer to the Certificate of Analysis.
Drug Formulation: To be determined
HS Tariff Code: 382200
How to use
In Vitro:
Heparin is a potent anticoagulant drug based on its ability to accelerate the rate at which antithrombin inhibits serine proteases in the blood coagulation cascade. Heparin and the structurally related heparan sulfate are complex linear polymers comprised of a mixture of chains of different length, having variable sequences. Heparin interactes most tightly with peptides containing a complementary binding site of high positive charge density. Heparin and heparan sulfate predominantly exhibit linear helical secondary structures with sulfo and carboxyl groups displayed at defined intervals and in defined orientations along the polysaccharide backbone. Heparin resembles DNA as both are highly charged linear polymers that behave as polyelectrolytes. Heparin is believed to function as an anticoagulant primarily through its interaction with AT III by enhancing AT-III-mediated inhibition of blood coagulation factors, including thrombin and factor Xa. Heparin binds to AT III and thrombin in a ternary complex, increasing the bimolecular rate constant for the inhibition of thrombin by a factor of 2000. Heparin is principally located in the granules of tissue mast cells that are closely associated with the immune response. Heparin makes numerous contacts with both FGF-2 and FGFR-1 stabilizing FGF–FGFR binding. Heparin also makes contacts with the FGFR-1 of the adjacent FGF–FGFR complex, thus seeming to promote FGFR dimerization.
References:
- Capila I, et al. Heparin-protein interactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2002 Feb 1;41(3):391-412.
- Anurag Purushothaman, et al. Fibronectin on the Surface of Myeloma Cell-derived Exosomes Mediates Exosome-Cell Interactions. J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 22;291(4):1652-63.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use.
Payment & Security
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.